
Get Cisco 400-007 Exam Dumps
Cisco Certified Design Expert CCDE v3.0 Exam Dumps
This Bundle Pack includes Following 3 Formats
Test software
Practice Test
Answers (PDF)

400-007 Desktop Practice
Test Software
Total Questions : 330

400-007 Questions & Answers
(PDF)
Total Questions : 330

400-007 Web Based Self Assessment Practice Test
Following are some 400-007 Exam Questions for Review
Refer to the exhibit.
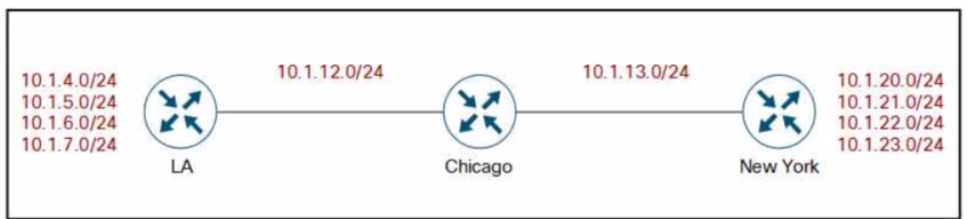
Company XYZ BGP topology is as shown in the diagram. The interface on the LA router connected toward the 10.1.5.0/24 network is faulty and is going up and down, which affects the entire routing domain. Which routing technique can be used in the routing policy design so that the rest of the network is not affected by the flapping issue?
A business wants to centralize services via VDI technology and to replace remote WAN desktop PCs with thin client-type machines to reduce operating costs Which consideration supports the new business requirement?
Company XYZ is running SNMPv1 in their network and understands that it has some flaws. They want to change the security design to implement SNMPv3 in the network Which network threat is SNMPv3 effective against?
What are two examples of components that are part of an SDN architecture? (Choose two.)
A customer migrates from a traditional Layer 2 data center network into a new SDN-based spine-and-leaf VXLAN EVPN data center within the same location The networks are joined to enable host migration at Layer 2 What is the final migration step after hosts have physically migrated to have traffic flowing through the new network without changing any host configuration?
Unlock All Features of Cisco 400-007 Dumps Software
Types you want
pass percentage
(Hours: Minutes)
Practice test with
limited questions
Support